Quality standards have become an integral part of how businesses function, influencing everything from product development to service delivery. But how do organisations consistently maintain and improve these standards over time? One approach is to employ skilled quality auditors who regularly assess processes for compliance. For those intrigued by the idea of conducting audits, one of the most direct pathways in Australia is to undertake a recognised qualification, like the BSB50920 Diploma of Quality Auditing. This article explores what a Diploma of Quality Auditing is, how it helps individuals transition into or advance within quality-focused careers, and why it remains relevant in today's marketplace.
Defining the Diploma of Quality Auditing
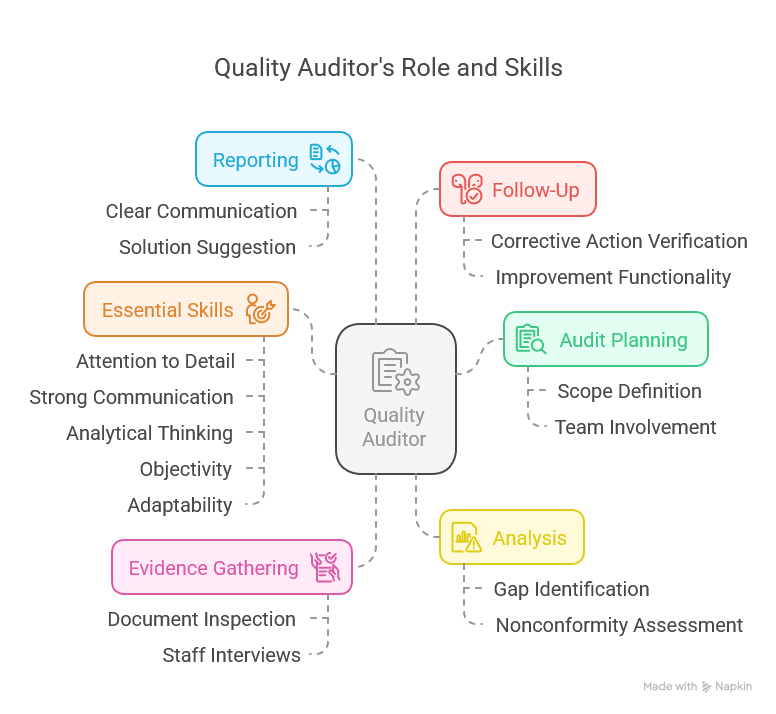
A Diploma of Quality Auditing is a vocational education and training course that provides learners with specialised knowledge of audit processes, compliance requirements, and continuous improvement frameworks. Although programs can differ between training providers, the core components typically include audit planning and implementation, risk management, reporting, and communication. The curriculum also aims to cultivate leadership attributes, especially for those who anticipate coordinating audit teams or liaising with senior stakeholders.
Within Australia, this diploma is governed by industry-endorsed standards. When you see the reference "BSB50920 Diploma of Quality Auditing," you know the qualification aligns with a specific training package that lays out the essential skills and knowledge for practice. According to the National Centre for Vocational Education Research (NCVER, 2021), courses that align with recognised training packages tend to yield strong outcomes for graduates, as their content is vetted and updated based on real industry feedback.
Why Choose a Diploma-Level Qualification?
Diplomas sit at a level of study that combines both theoretical and hands-on learning. This approach suits individuals who want to gain practical auditing skills, as opposed to courses that are purely academic. Additionally, a diploma might be more manageable for those already working who need a part-time or flexible study schedule. For a person eyeing a transition into auditing from a trades background, the structured nature of a diploma can be beneficial, because it lays out clear, step-by-step pathways.
While shorter certificates exist in auditing or compliance, a diploma typically offers broader coverage, venturing into topics such as audit planning, corrective action processes, and leadership. Many employers look favourably on diploma holders because they see it as evidence of advanced skills, as well as a willingness to engage in detailed study and practical application.
Core Components of the Diploma
Though the exact structure of study varies by provider, a Diploma of Quality Auditing generally addresses:
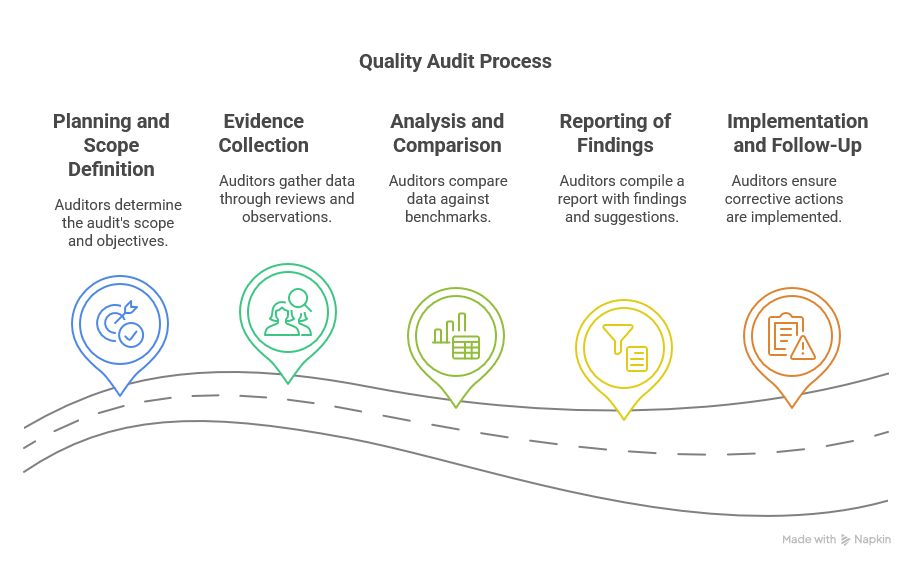
Audit Planning and Scheduling
Students learn how to determine an audit's objectives, scope, and methodology. This includes understanding timelines, necessary resources, and which stakeholders to involve. Proper planning not only helps in meeting compliance requirements but also aids in spotting opportunities for process improvements.
Conducting the Audit
Carrying out an audit involves gathering evidence, reviewing documents, interviewing staff, and observing workflows. This stage is about data collection and objective evaluation. Students become familiar with techniques that guide them in identifying discrepancies without disrupting daily operations.
Analysis and Reporting
Information gathered during the audit must be carefully analysed. This often means comparing current practices to set standards. Learners discover how to translate data into clear reports, highlighting both compliance achievements and areas requiring corrective measures. The ability to provide persuasive and actionable reports is highly valued in the workplace.
Corrective Actions and Continuous Improvement
A key outcome of any quality audit is to recommend or implement improvements. While some courses focus heavily on compliance audits, many also emphasise the continuous improvement cycle. This means identifying root causes of noncompliance or inefficiencies, suggesting corrective measures, and tracking their implementation.
Leadership and Team Management
Audits rarely happen in isolation. It is common for a lead auditor or audit manager to coordinate tasks across departments. As a result, leadership modules are often included to help learners confidently steer an audit project, communicate expectations, and manage potential resistance from teams being audited.
When combined, these competencies ensure graduates can handle an end-to-end audit process, from setting objectives to verifying that follow-up actions have been integrated.
Importance of Industry and Government Recognition
One of the reasons this diploma stands out among quality auditing courses is its industry recognition. Businesses value the structure and rigour built into qualifications endorsed by training authorities and the Australian Government. Industry and government bodies contribute to the training package that underpins the BSB50920 Diploma, ensuring it reflects real-world priorities.
Potential students sometimes ask if the diploma is just a piece of paper or if it genuinely makes a difference in employability. Feedback from both employers and graduates suggests that practical courses with a strong link to industry standards tend to produce job-ready professionals (Australian Skills Quality Authority, 2023). While experience always matters, a diploma can open doors by demonstrating formal competence in planning and executing audits.
Entry Requirements and Pathways
Some providers do not have strict prerequisites, but they typically recommend relevant work experience in a business or compliance setting. This could be a few years of employment in any role that deals with regulations, customer standards, or operational guidelines. Tradespeople, for example, might draw on their experience of following building codes or safety regulations when stepping into the auditing arena.
Upon completion of a Diploma of Quality Auditing, learners may go on to pursue advanced diplomas or other higher-level qualifications in business or compliance. They may also enrol in short courses that specialise in areas such as environmental auditing or data security. This broad range of possible next steps shows how the diploma can be a cornerstone of continued professional development.
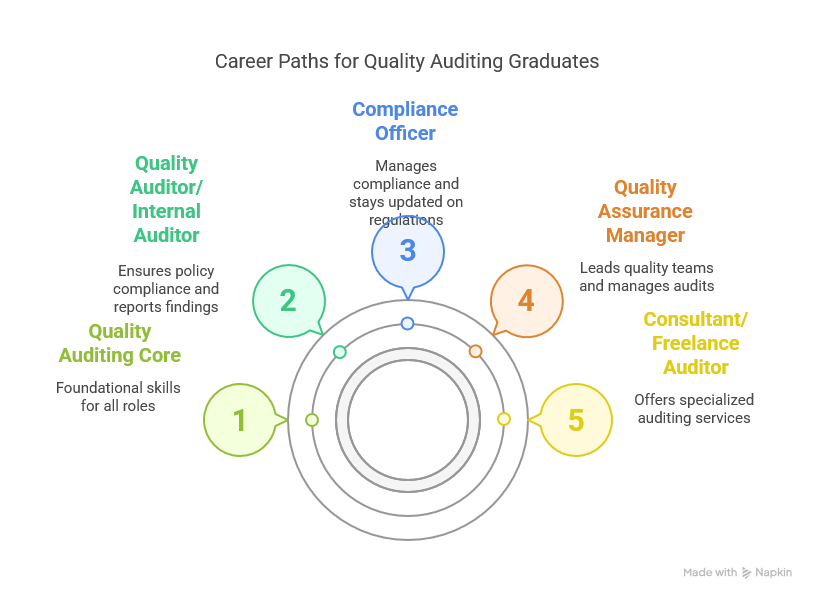
Career Trajectories
Graduates from a Diploma of Quality Auditing often find work in positions like:
Quality Auditor or Internal Auditor
These roles involve conducting regular checks within an organisation to ensure that internal policies align with regulations. Internal auditors frequently communicate findings to senior management, influencing key decisions about risk and resource allocation.
Compliance Officer
Some businesses merge internal auditing with broader compliance responsibilities, including staying up to date on new regulations. A diploma can lay the groundwork for such roles, helping professionals understand the complexities of different legal frameworks.
Quality Assurance Manager
In this capacity, individuals lead broader quality teams, manage policy implementation, and coordinate external audits. While managerial roles sometimes require years of experience, a relevant diploma can be an important stepping stone.
Consultant or Freelance Auditor
Those with an entrepreneurial mindset sometimes offer auditing services on a contract basis. This can be appealing for professionals who prefer variety in their projects or want to specialise in a particular industry.
Workplace Relevance
Every industry in Australia has some level of regulation. Food and beverage companies adhere to safety standards, construction projects follow building codes, healthcare organisations must comply with stringent patient care guidelines, and so on. The universal need for compliance and quality means that a formal qualification in quality auditing can hold weight across diverse sectors. Additionally, many businesses in regulated fields see routine audits as a way to remain competitive. They rely on skilled auditors to maintain certifications and demonstrate excellence to stakeholders.
According to trends reported by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO, 2022), there has been a steady increase in certifications like ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems) worldwide. Auditors familiar with multiple frameworks are in demand because they help organisations meet these evolving standards. Hence, pursuing this diploma can be a solid investment for those aiming to stay relevant in industries with rising compliance obligations.
Common Concerns and Misconceptions
It's not unusual for potential students to wonder if a Diploma of Quality Auditing is too specific and might limit their career options. In reality, auditing underpins a wide range of roles in business, healthcare, education, government, and beyond. The skills learned—research, analysis, problem-solving, communication—are transferable and often applicable to roles involving quality management, regulatory oversight, or policy review.
Another concern is that auditing might be tedious or purely documentation-based. While documentation is a component, modern audits increasingly incorporate proactive strategies, technology, and real-time data analysis. Many audit professionals describe their work as investigative and collaborative, involving communication with multiple departments and stakeholders.
Online or In-Person Study Options
Training providers often offer flexible modes of study, including online, blended, or in-person classes. Online courses can be attractive if you are balancing work, family, or other commitments. They typically use digital platforms for modules and virtual collaboration, giving you the chance to interact with other students remotely. In-person classes, meanwhile, may offer more immediate access to trainers, with the benefit of practical, group-based activities. The choice depends on personal preference, learning style, and availability.
Assessments in a Diploma of Quality Auditing
Assessment tasks can take several forms, including case studies, role-plays, quizzes, and workplace-based projects. For instance, you might simulate an audit scenario where you interview mock employees, evaluate documentation, and produce an audit report. These tasks provide an authentic taste of the real working environment, teaching you how to handle common challenges like incomplete records or uncooperative staff.
Because of the practical element, many training providers encourage or require that you undertake some fieldwork. This might mean auditing a small process at your current workplace or collaborating with a host organisation. Such experiences can build confidence, develop communication skills, and help you understand the nuances of real-life auditing situations.
The Link to Continuous Improvement
While some qualifications focus exclusively on compliance, a Diploma of Quality Auditing normally highlights how compliance can spur innovation and improvement. Auditing teams often identify inefficiencies, recommend new workflows, or suggest the adoption of better tools. Over time, this helps the organisation refine its practices, enhancing both quality and cost-effectiveness.
This focus on continuous improvement can be deeply satisfying for individuals who wish to influence positive change in their workplace. Rather than merely identifying non-compliant issues, quality auditors aim to work collaboratively, guiding departments toward higher standards. It's an approach that requires strong interpersonal skills alongside technical auditing know-how.
Comparing Different quality auditing courses
Prospective students have multiple options when looking into quality auditing courses. Some courses focus narrowly on specific frameworks, like ISO 9001, while others might be shorter certificate programs more appropriate for frontline staff who handle basic auditing tasks. The advantage of a comprehensive diploma is that it goes beyond isolated frameworks. It teaches universal principles that can apply to multiple standards or regulations. This broad base of knowledge equips you to adapt to varied organisational contexts.
In addition to technical breadth, a diploma often includes modules on leadership, communication, and project management—skills indispensable for senior auditing roles. According to data from the Australian Skills Quality Authority (ASQA, 2023), well-rounded courses that blend auditing procedures with soft skills produce graduates who excel at building consensus and driving improvement initiatives.
How to Decide If It's Right for You
Individuals drawn to analytical work and problem-solving often find auditing fulfilling. If you like dissecting processes, identifying gaps, and building solutions, this diploma might be a natural fit. It can also be an asset if you have an eye on management roles, as the qualification positions you to deal effectively with compliance and quality at a broader organisational level.
However, it's wise to consider your existing background. Those completely new to business processes might experience a steeper learning curve. Similarly, if you're already working in a compliance role and want formal recognition for your skills, this diploma can validate and enhance your career prospects.
A Diploma of Quality Auditing is a comprehensive, vocationally oriented qualification that teaches the fundamentals of auditing, reporting, team management, and continuous improvement. It suits individuals who want to specialise in compliance-related roles, as well as those hoping to strengthen their career prospects with a formal credential.
By exploring audit principles in detail, graduates leave the course prepared to support or lead audit efforts in a range of organisational settings. If you're keen on exploring more about the auditing profession or the broader field of quality management, be sure to check out the main article, "BSB50920 Diploma in Quality Auditing: Is This the Right Qualification for Your Career Path?" You may also want to explore the related sub-articles that dive deeper into what a quality auditor actually does and what QA accreditation entails. Connecting with a reputable training provider is another strong step, as they can answer specific questions about study modes, pricing, or any prerequisites. Taking that initial step could put you on the path to a fulfilling and impactful role in quality assurance and auditing.